
In a previous couple of tutorials, we created a Spring boot project and Built CRUD Restful web services with
DTO.
Refer to previous tutorials:
Spring
Boot 3 CRUD RESTful WebServices with MySQL Database
Spring Boot DTO Example Tutorial
In this tutorial, we will learn how to use the ModelMapper library to map the JPA entity into DTO and vice
versa.
ModelMapper is a lightweight Java library used for object mappings.
The goal of ModelMapper is to make object mapping easy, by automatically determining how one object model
maps to another, based on conventions, in the same way, that a human would - while providing a simple,
refactoring-safe API for handling specific use cases.
Read more about ModelMapper at the official website: http://modelmapper.org/getting-started/
This tutorial is a continuation of below two tutorials so first, create CRUD REST APIs using below tutorials:
Spring Boot 3 CRUD RESTful WebServices with MySQL Database
Spring Boot DTO Example Tutorial
Check out the complete source code of this tutorial is available on my GitHub repository at Spring Boot CRUD
RESTful WebServices
1. Add Maven Dependency
2. Configure ModelMapper class a Spring Bean
3. Inject and Use ModelMapper Spring Bean in Service Class
4. Test CRUD REST APIs using Postman client
Open the pom.xml file and add the following ModelMapper dependency:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.modelmapper/modelmapper -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.modelmapper</groupId>
<artifactId>modelmapper</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>Next, let's configure ModelMapper class as Spring bean in the main entry point class of the Spring Boot application:
package net.javaguides.springboot;
import org.modelmapper.ModelMapper;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootRestfulWebservicesApplication {
@Bean
public ModelMapper modelMapper(){
return new ModelMapper();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootRestfulWebservicesApplication.class, args);
}
}We have configured ModelMapper as Spring bean using Java-based configuration:
@Bean
public ModelMapper modelMapper(){
return new ModelMapper();
}Next, let's inject ModelMapper Spring bean in UserServieImpl class and use it's methods to convert the User JPA entity into UserDto and vice versa:
package net.javaguides.springboot.service.impl;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import net.javaguides.springboot.dto.UserDto;
import net.javaguides.springboot.entity.User;
import net.javaguides.springboot.exception.EmailAlreadyExistsException;
import net.javaguides.springboot.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import net.javaguides.springboot.mapper.UserMapper;
import net.javaguides.springboot.repository.UserRepository;
import net.javaguides.springboot.service.UserService;
import org.apache.logging.log4j.util.Strings;
import org.modelmapper.ModelMapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Service
@AllArgsConstructor
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private UserRepository userRepository;
private ModelMapper modelMapper;
@Override
public UserDto createUser(UserDto userDto) {
// Convert UserDto into User JPA Entity
// User user = UserMapper.mapToUser(userDto);
User user = modelMapper.map(userDto, User.class);
User savedUser = userRepository.save(user);
// Convert User JPA entity to UserDto
//UserDto savedUserDto = UserMapper.mapToUserDto(savedUser);
UserDto savedUserDto = modelMapper.map(savedUser, UserDto.class);
return savedUserDto;
}
@Override
public UserDto getUserById(Long userId) {
User user = userRepository.findById(userId).get();
//return UserMapper.mapToUserDto(user);
return modelMapper.map(user, UserDto.class);
}
@Override
public List< UserDto> getAllUsers() {
List< User> users = userRepository.findAll();
// return users.stream().map(UserMapper::mapToUserDto)
// .collect(Collectors.toList());
return users.stream().map((user) -> modelMapper.map(user, UserDto.class))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
@Override
public UserDto updateUser(UserDto user) {
User existingUser = userRepository.findById(user.getId()).get();
existingUser.setFirstName(user.getFirstName());
existingUser.setLastName(user.getLastName());
existingUser.setEmail(user.getEmail());
User updatedUser = userRepository.save(existingUser);
//return UserMapper.mapToUserDto(updatedUser);
//return modelMapper.map(updatedUser, UserDto.class);
}
@Override
public void deleteUser(Long userId) {
userRepository.deleteById(userId);
}
}That's it. Next, let's run the Spring boot application and test all the CRUD REST APIs.
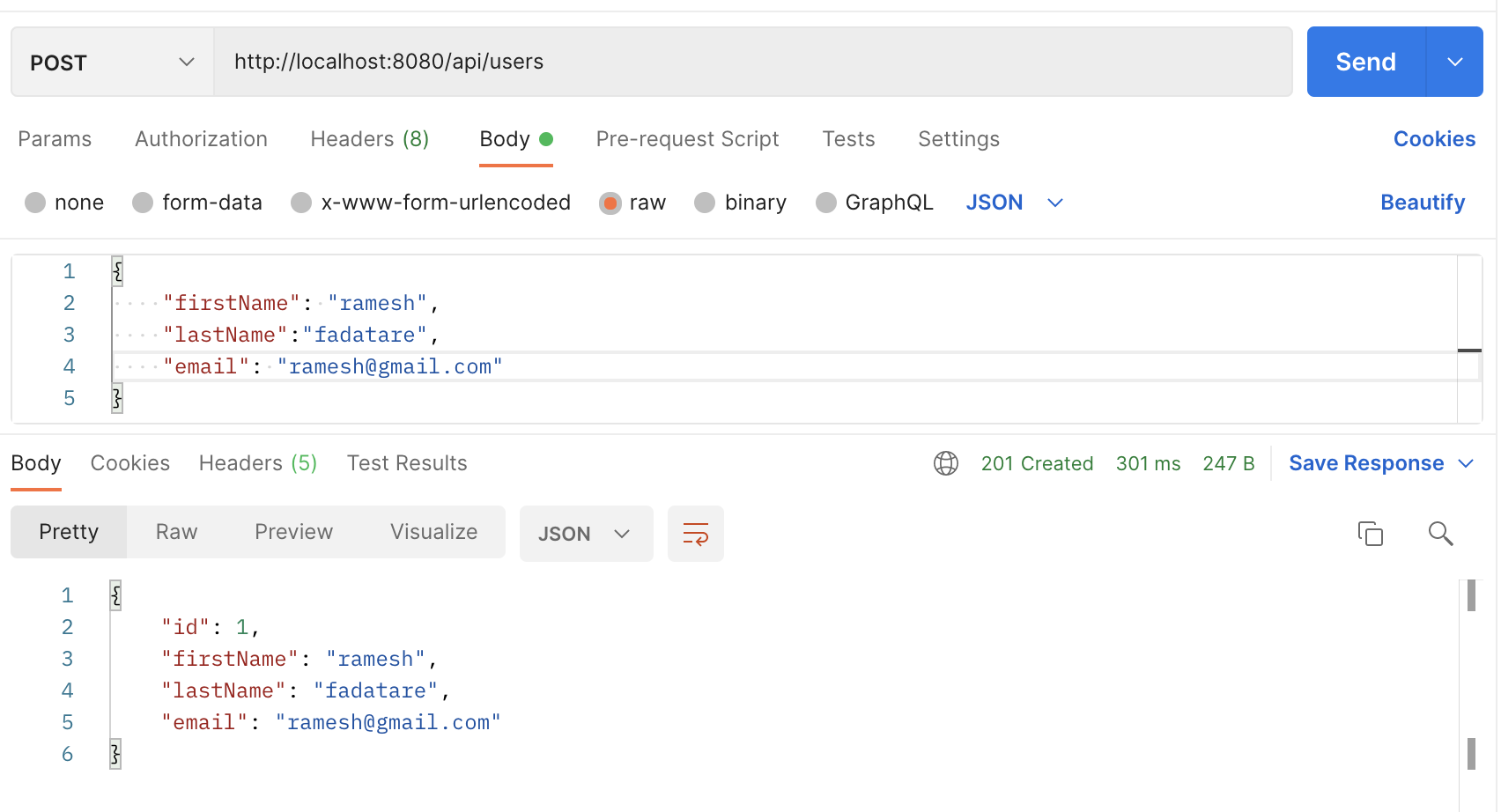
Request URL: http://localhost:8080/api/users
HTTP Method: POST
Request Body:
{
"firstName": "ramesh",
"lastName":"fadatare",
"email": "ramesh@gmail.com"
}Refer to this screenshot to test Create User REST API:
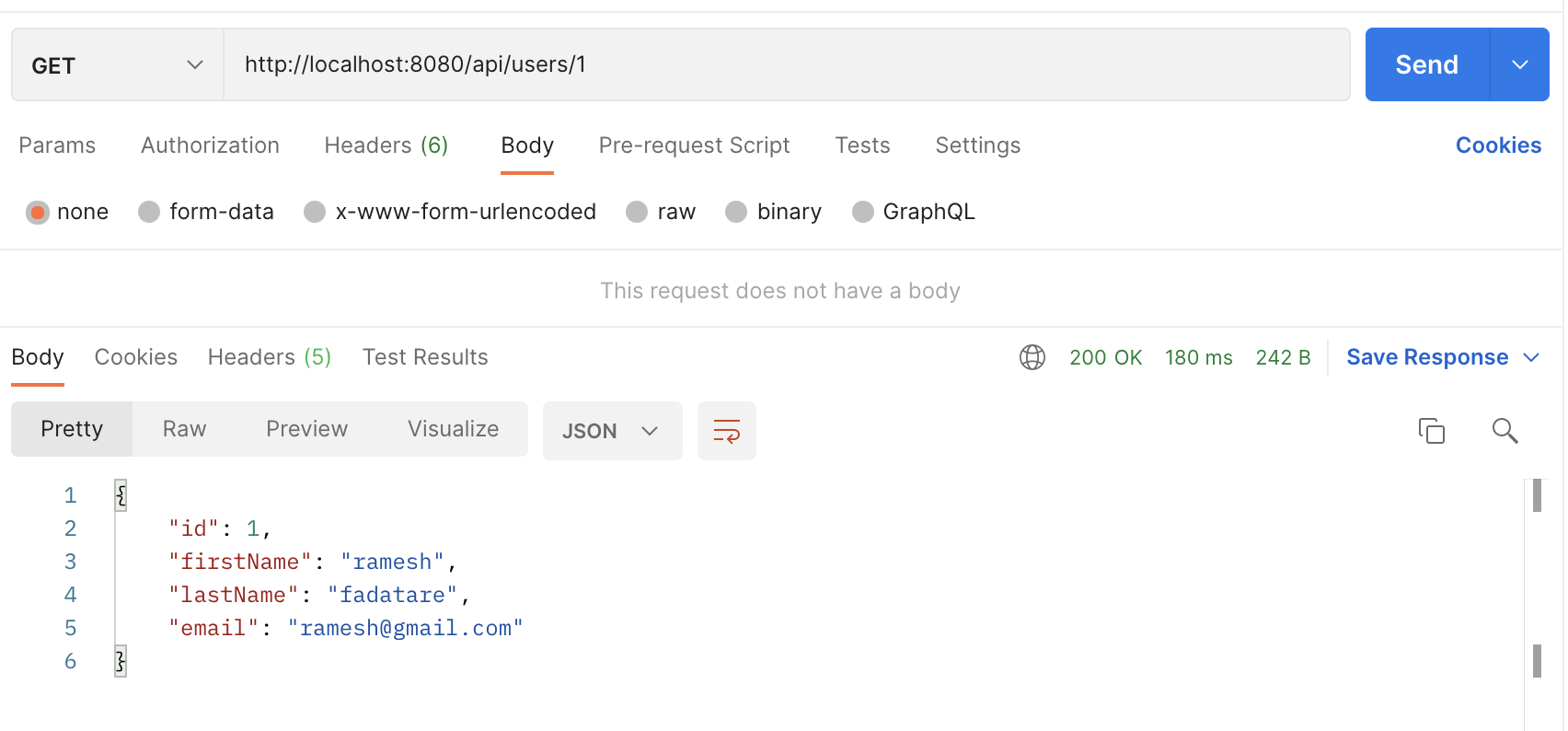
Request URL: http://localhost:8080/api/users/1
HTTP Method: GET
Refer to this screenshot to test GET User REST API:
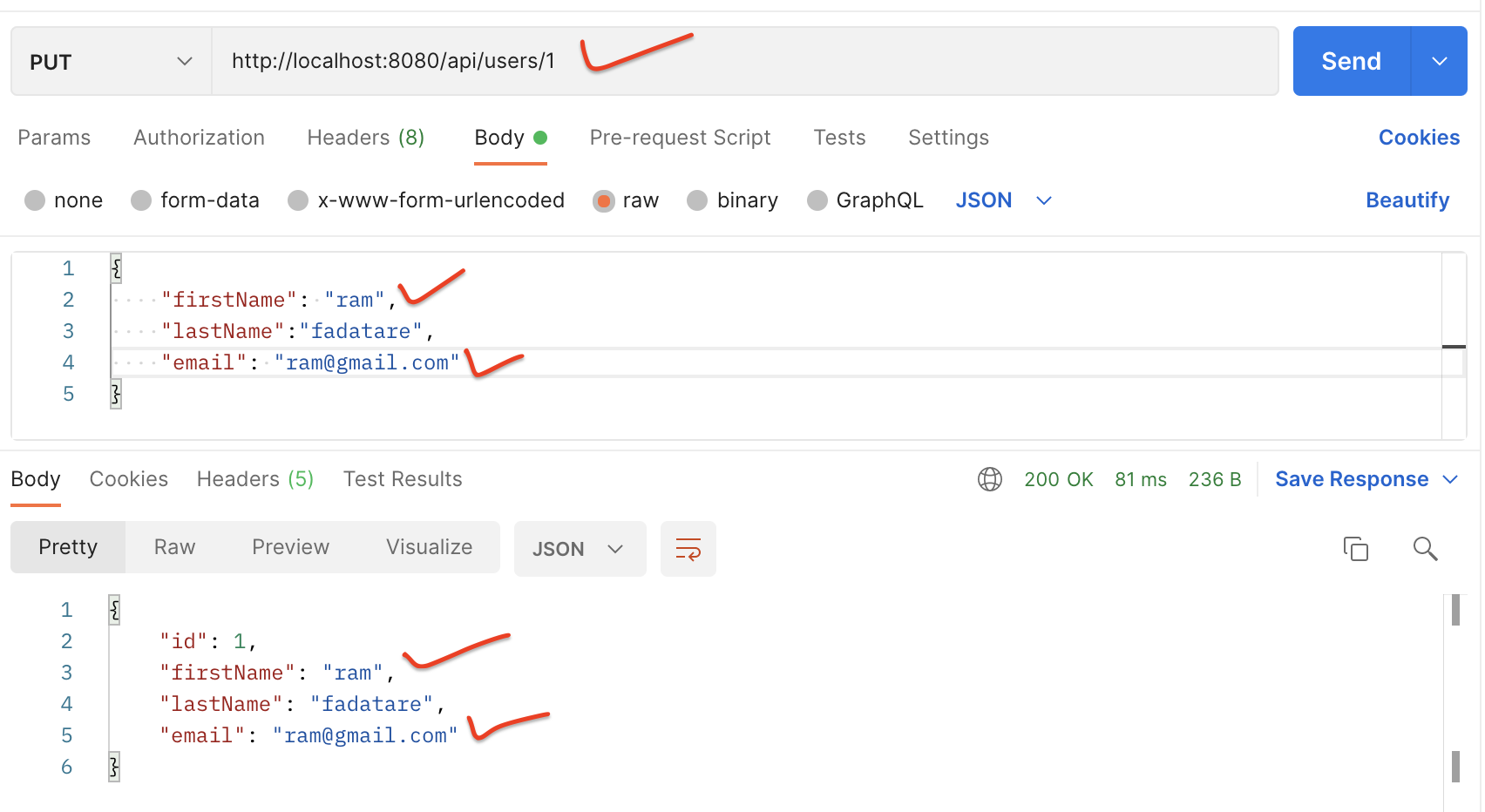
Request URL: http://localhost:8080/api/users/1
HTTP Method: PUT
Request Body:
{
"firstName": "ram",
"lastName":"fadatare",
"email": "ram@gmail.com"
}
Request URL: http://localhost:8080/api/users
HTTP Method: GET
Refer to this screenshot to test GET All User REST API:
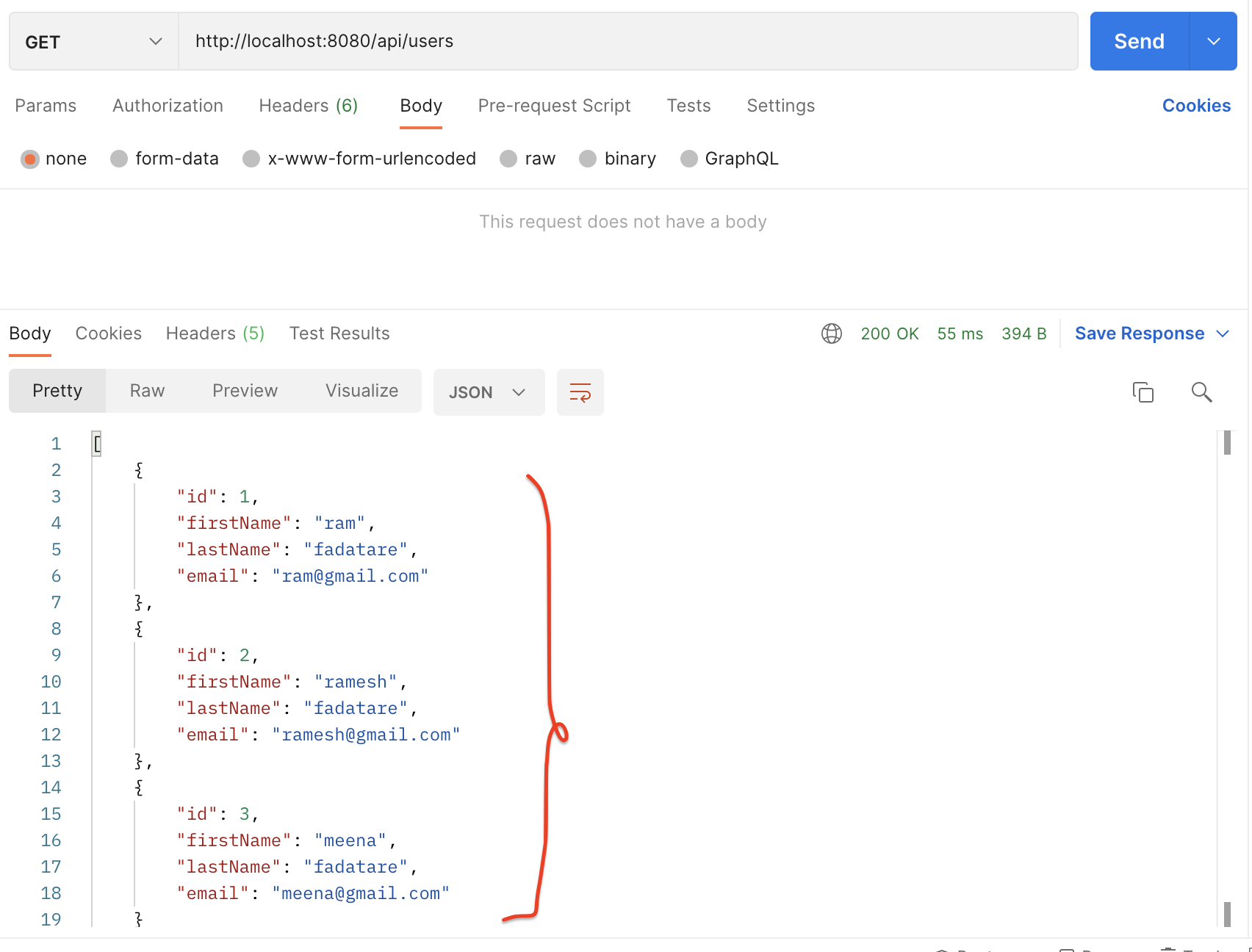
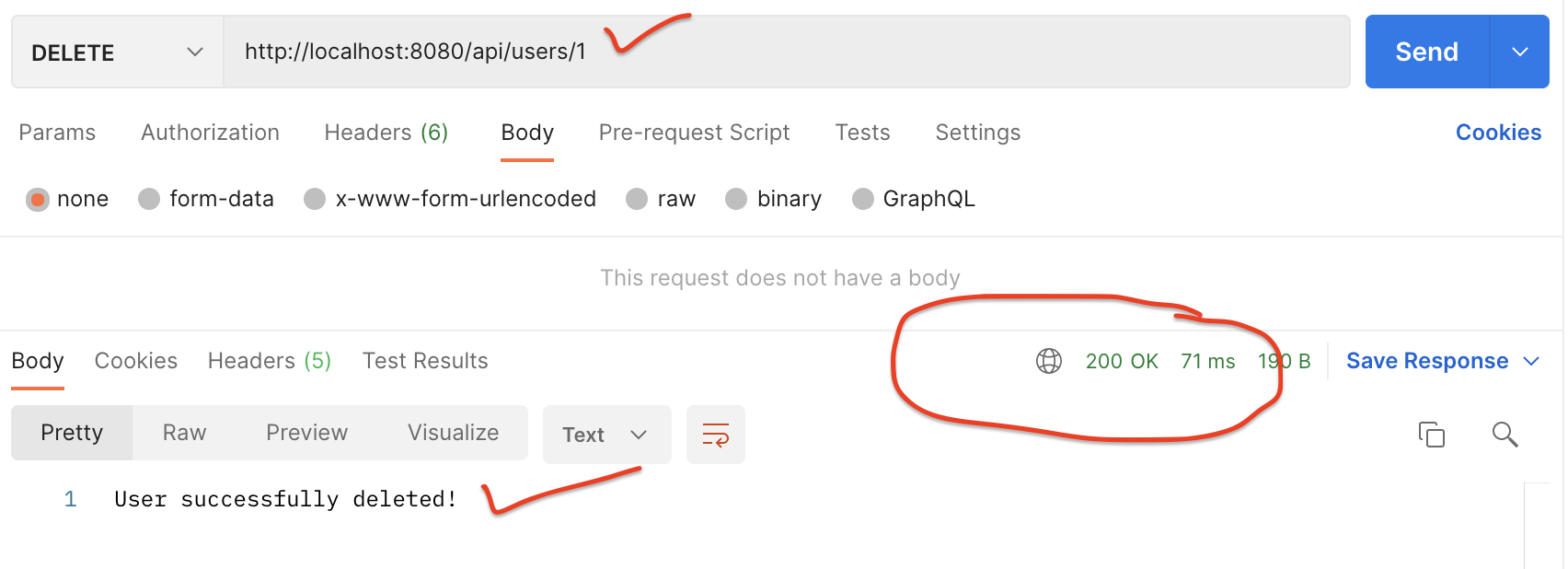
Request URL: http://localhost:8080/api/users/1
HTTP Method: DELETE
Refer to this screenshot to test Delete User REST API:
The source code of this tutorial is available on my GitHub repository at Spring Boot CRUD RESTful WebServices
In this tutorial, we have seen how to use the ModelMapper library to convert JPA entity into DTO and vice versa in the Spring boot application.